Loading... # 在Ubuntu上查看PCI-E插槽与版本 ## PCI-E简介 PCI-Express(peripheral component interconnect express)是一种高速串行计算机扩展总线标准,它原来的名称为“3GIO”,是由英特尔在2001年提出的,旨在替代旧的PCI,PCI-X和AGP总线标准。 在目前的电脑主要提供种规格的插槽。 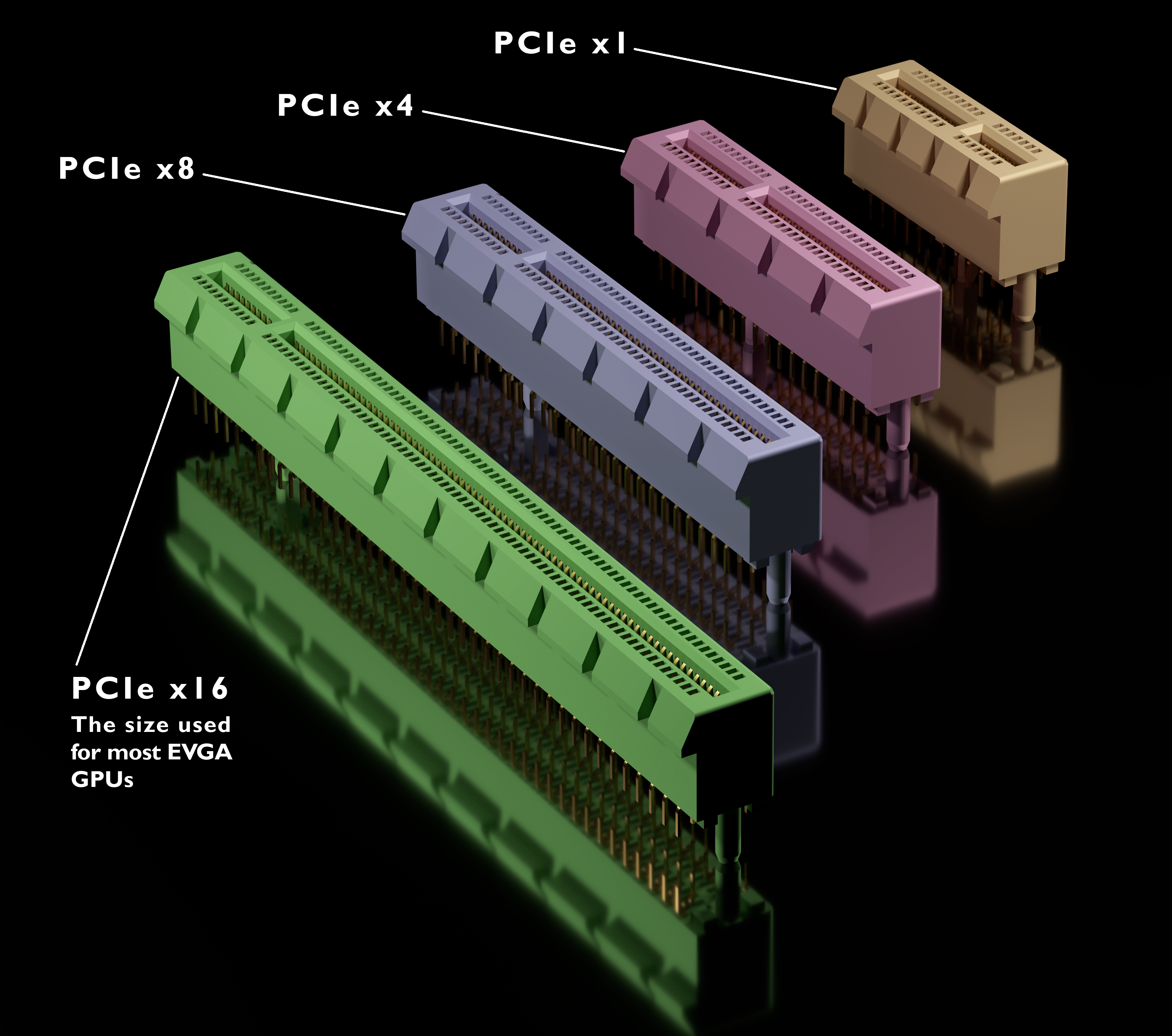 ## 在Linux(Ubuntu)查看详细信息 #### 通过DMI信息查看主板上的PCI-E插槽 ``` root@user:~# dmidecode | grep --color "PCI" PCI is supported Designation: PCIe Slot 3 Designation: PCIe Slot 2 Designation: PCIe Slot 7 Designation: PCIe Slot 6 ``` 这是一台戴尔的2U机架式服务器,它只可以看到不同PCI-E的插槽编号,因为它可以通过Riser卡来更改功能,所以关于不同版本的PCI-E插槽信息并不详细,下面来看一下一台组装机的信息。 ``` root@user:~# dmidecode | grep --color "PCI" PCI is supported Designation: PCIE1 Type: x16 PCI Express Designation: PCIE2 Type: x16 PCI Express Designation: PCIE3 Type: x16 PCI Express Designation: PCIE4 Type: x16 PCI Express Descriptor 9: PCI parity error Descriptor 10: PCI system error ``` 这台组装机上返回的信息可以看到,PCIE1-PCIE4都是x16插槽。 #### PCIe各版本与速率 | PCI Express 版本 | 编码方案 | 传输速率 | 吞吐量 | | | | | ---------------- | --------- | ------------ | --------------- | ---------------- | ---------------- | ---------------- | | -| - | -| ×1 | ×4 | ×8 | ×16 | | 1 | 8b/10b | 2.5GT/s | 250MB/s | 1GB/s | 2GB/s | 4GB/s | | 2 | 8b/10b | 5GT/s | 500MB/s | 2GB/s | 4GB/s | 8GB/s | | 3 | 128b/130b | 8GT/s | 984.6MB/s | 3.938GB/s | 7.877GB/s | 15.754GB/s | | 4 | 128b/130b | 16GT/s | 1.969GB/s | 7.877GB/s | 15.754GB/s | 31.508GB/s | | 5 | 128b/130b | 32 or 25GT/s | 3.9 or 3.08GB/s | 15.8 or 12.3GB/s | 31.5 or 24.6GB/s | 63.0 or 49.2GB/s | #### PCIe传输量与吞吐量 传输速率为每秒传输量GT/s,而不是每秒位数Gbps,因为传输量包括不提供额外吞吐量的开销位; 比如PCIe 1.x和PCIe 2.x使用8b/10b编码方案,导致占用了20% (= 2/10)的原始信道带宽。 GT/s —— Giga transation per second (千兆传输/秒),即每一秒内传输的次数。重点在于描述物理层通信协议的速率属性,可以不和链路宽度等关联。 Gbps —— Giga Bits Per Second (千兆位/秒)。GT/s 与Gbps 之间不存在成比例的换算关系。 PCIe 吞吐量(可用带宽)计算方法: 吞吐量 = 传输速率 * 编码方案 例如:PCI-e2.0 协议支持 5.0 GT/s,即每一条Lane上支持每秒钟内传输5G个Bit;但这并不意味着 PCIe 2.0协议的每一条Lane支持 5Gbps 的速率。 为什么这么说呢?因为PCIe 2.0 的物理层协议中使用的是8b/10b的编码方案。 即每传输8个Bit,需要发送10个Bit;这多出的2个Bit并不是对上层有意义的信息。 那么,PCIe 2.0协议的每一条Lane支持 5 * 8 / 10 = 4 Gbps = 500 MB/s 的速率。 以一个PCIe 2.0 x8的通道为例,x8的可用带宽为 4 * 8 = 32 Gbps = 4 GB/s。 PCI-e3.0 协议支持 8.0 GT/s, 即每一条Lane 上支持每秒钟内传输 8G个Bit。 而PCIe 3.0 的物理层协议中使用的是 128b/130b 的编码方案。 即每传输128个Bit,需要发送130个Bit。 那么, PCIe 3.0协议的每一条Lane支持 8 * 128 / 130 = 7.877 Gbps = 984.6 MB/s 的速率。 一个PCIe 3.0 x16的通道,x16 的可用带宽为 7.877 * 16 = 126.031 Gbps = 15.754 GB/s。 #### Linux下查看PCIe的详细信息 在 Linux 下要如何得知 PCI-E Bus 使用的是 Gen(Generation) 1 還是 Gen2 還是新一代的 Gen 3 雖然使用 `lspci`只可以看到目前系統所有的裝置.但是好像看不到 PCI-E Bus 所採用的是哪一代的 PCI-E. ``` root@xjwx:~# lspci 00:00.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse Root Complex 00:00.2 IOMMU: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse IOMMU ...... e4:00.0 Non-Essential Instrumentation [1300]: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse Reserved SPP e4:00.2 Encryption controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse PTDMA ``` 当然上面的信息我只放了前后几行,因为这台机器上有着非常多的设备,实在过于冗长。 如果信息不利于阅读,也可以通过树状关系来查看。 ``` root@xjwx:~# lspci -tv -+-[0000:e0]-+-00.0 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse Root Complex | +-00.2 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse IOMMU ...... | \-00.3 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship USB 3.0 Host Controller \-[0000:00]-+-00.0 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Starship/Matisse Root Complex ``` 当然,这也非常的长,就放几行意思一下就好了,大家如果感兴趣,可以查看自己的开发环境和生产环境设备。 接下来就查看下关于显卡的PCIe信息,因为本文的初始是因为,我采用了PCIE延长线来接了30系显卡,但是无法正常驱动,所以,才来补充学习这方面的知识,下面就来模拟一下我边学习边分析的过程。 查看NVIDIA显卡的PCIe信息: ``` root@user:~# lspci | grep -i nvi 21:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GA102 [GeForce RTX 3080] (rev a1) 21:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation Device 1aef (rev a1) e2:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GA102 [GeForce RTX 3080] (rev a1) e2:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation Device 1aef (rev a1) ``` 这里因为我更新了`pciids`,所以可以直接看到显卡的型号,关于这部分可以看一下前面的小记:<div class="preview"> <div class="post-inser post box-shadow-wrap-normal"> <a href="https://blog.yelvlab.cn/archives/597/" target="_blank" class="post_inser_a no-external-link no-underline-link"> <div class="inner-image bg" style="background-image: url(https://pic-up.yelvlab.cn/nvidia-logo.jpg);background-size: cover;"></div> <div class="inner-content" > <p class="inser-title">Linux查看显卡型号(可类推其他PCIE设备)</p> <div class="inster-summary text-muted"> Linux查看显卡型号可以通过查看PCI设备来看显卡型号:lspci | grep -i nvidia -----... </div> </div> </a> <!-- .inner-content #####--> </div> <!-- .post-inser ####--> </div> 回到正题,Linux下使用三个编号来识别区分每个PCI设备,分别为: 1. bus number:8bits 2^8 至多可连接256个总线(0 to ff) 2. device number:5bits 2^5 至多连接32种设备(0 to 1f) 3. function number:3bits 2^3 至多每个设备可有8项功能(0 to 7) 想要查看更详细的信息,就需要线找到我们关心的设备的VID(Vendor ID)和PID(Product ID): ``` root@user:~# lspci -n | grep -i 21:00.0 21:00.0 0300: 10de:2206 (rev a1) ``` Linux使用Class ID + Vendor ID + Product ID 来表示设备,可以看到刚刚看的一张显卡对应的信息为:`Class ID:0300,Vendor ID:10de,Product ID:2206` 最后,再来查看指定设备的PCI带宽: ``` root@user:~# lspci -n -d 10de:2206 -vvv | grep --color Width LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 16GT/s, Width x16, ASPM L0s L1, Exit Latency L0s <1us, L1 <4us LnkSta: Speed 8GT/s, Width x16, TrErr- Train- SlotClk+ DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt- LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 16GT/s, Width x16, ASPM L0s L1, Exit Latency L0s <1us, L1 <4us LnkSta: Speed 8GT/s, Width x16, TrErr- Train- SlotClk+ DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt- ``` LnkSta : 目前设备所提供的速度 PCI-Express 2.0 ( 8GT/s ) LnkCap : 查看的设备支持的速度 LnkSta 和 LnkCap 这两个值可能不一样,这也是本次学习的主要目的,确认了这条PCIe Last modification:December 24, 2020 © Allow specification reprint Like 0 If you think my article is useful to you, please feel free to appreciate